1-D Scatter Plots with Confidence Intervals Using ggplot2
geom_stripchart.Rdgeom_stripchart is an adaptation of the EnvStats function
stripChart and is used to create a strip plot
using functions from the package ggplot2.
geom_stripchart produces one-dimensional scatter plots (also called dot plots),
along with text indicating sample size and estimates of location (mean or median) and scale
(standard deviation or interquartile range), as well as confidence intervals
for the population location parameter, and results of a hypothesis
test comparing group locations.
geom_stripchart(..., seed = 47, paired = FALSE, paired.lines = paired,
group = NULL, x.nudge = if (paired && paired.lines) c(-0.3, 0.3) else 0.3,
text.box = FALSE, location = "mean", ci = "normal", digits = 1,
digit.type = "round", nsmall = ifelse(digit.type == "round", digits, 0),
jitter.params = list(), point.params = list(), line.params = list(),
location.params = list(), errorbar.params = list(),
n.text = TRUE, n.text.box = text.box, n.text.params = list(),
location.scale.text = TRUE, location.scale.text.box = text.box,
location.scale.text.params = list(), test.text = FALSE,
test.text.box = text.box,
test = ifelse(location == "mean", "parametric", "nonparametric"),
test.text.params = list())Arguments
- ...
Arguments that can be passed on
layer, as well as to the geoms and stats used to create the strip chart, includinggeom_jitter,geom_point,geom_line,stat_summary,geom_errorbar,stat_n_text,stat_mean_sd_text,stat_median_iqr_text, andstat_test_text.- seed
For the case of non-paired data, the argument
seedis passed to the R functionset.seed. Because jittering depends on the R random number generator, using the same value ofseedeach time the same data are plotted withgeom_stripchartensures that the resulting plot is the same. The default value isset.seed=47.- paired
For the case of two groups, a logical scalar indicating whether the data should be considered to be paired. The default value is
paired=FALSE. Whenpaired=TRUE, you must also supply the argumentgroup(see below) to indicate which variable to use to identify the pairing (e.g., a variable that indicates which observations were taken before treatment and which observations were taken after treatment).NOTE: if the argument
test.text.paramsis supplied and it includes a component namedpaired, the value of that component is overriden by the value of the argumentpaired.- paired.lines
For the case when there are two groups and the observations are paired (i.e.,
paired=TRUE), a logical scalar indicating whether to draw lines between the paired observations. The default value is the value ofpaired.- group
For the case when there are two groups and the observations are paired (i.e.,
paired=TRUE), a character string indicating the variable that identifies the pairing (e.g., a variable that indicates which observations were taken before treatment and which observations were taken after treatment).- x.nudge
A numeric scalar indicating the amount to move the estimates of location and confidence interval lines on the \(x\)-axis to the right or left of the actual \(x\) value. This is used to avoid overlapping with the actual data. For the case of two groups and paired observations, the default value is
x.nudge=c(-0.3, 0.3), which draws estimates of location and confidence interval lines to the left by 0.3 for the first group and to the right by 0.3 for the second group. Otherwise, the default value isx.nudge=0.3.- text.box
A logical scalar indicating whether to surround text indicating sample size, location/scale estimates, and test results with text boxes (i.e., whether to use
link[ggplot2]{geom_label}instead ofgeom_text). This is a convenience argument and is simply a way to simultaneously set the values ofn.text.box,location.scale.text.box, andtest.text.box. You can override this argument for sample size, location/scale, and/or test results by supplying the argumentsn.text.box,location.scale.text.box, andtest.text.boxindividually (see below).- location
A character string indicating whether to display the mean for each group
(location="mean", the default) or the median for each group (location="median").- ci
For the case when
location="mean", a character string indicating what kind of confidence interval to plot for each group. Possible values areci="normal"(standard confidence interval based on Student's t-distribution; the default), orci="boot"(confidence interval based on the bootstrap).NOTE: For the case when
location="median", quantiles are plotted. By default, the 25'th and 75'th percentiles are plotted, but this can be changed via including a component calledconf.intin the argumenterror.bar.params. See the help file forsmedian.hilowfor details.- digits
Integer indicating the number of digits to use for displaying text indicating the location and scale estimates and, for the case of one or two groups, the number of digits to use for displaying text indicating the confidence interval associated with the test of hypothesis. When
digit.type="round"(see below) the argumentdigitsindicates the number of digits to round to, and whendigit.type="signif"the argumentdigitsindicates the number of significant digits to display. The default value isdigits=1.For location/scale estimates, you can override the value of this argument by including a component named
digitsin the argumentlocation.scale.text.params, and for confidence interval limits, you can override the value of this argument by including a component namedlocation.digitsin the argumenttest.text.params.- digit.type
Character string indicating whether the
digitsargument (see above) refers to significant digits (digit.type="signif"), or how many decimal places to round to (digit.type="round", the default).For location/scale estimates, you can override the value of this argument by including a component named
digit.typein the argumentlocation.scale.text.params, and for confidence interval limits, you can override the value of this argument by including a component namedlocation.digit.typein the argumenttest.text.params.- nsmall
Integer passed to the function
formatindicating the the minimum number of digits to the right of the decimal point for the computed estimates of location and scale and the confidence interval associated with the test of hypothesis. The default value isnsmall=digitswhendigit.type="round"andnsmall=0whendigit.type="signif". Whennsmallis greater than 0, all computed estimates of location and scale and all confidence interval limits will have the same number of digits to the right of the decimal point (including, possibly, trailing zeros). To omit trailing zeros, setnsmall=0.- jitter.params
A list containing arguments to the function
geom_jitterthat will be used to plot the points. The default value is an empty list:jitter.params=list(), in which case the default values forgeom_jitterare used, except for the following modifications:pch=1, width=0.15, height=0.This argument is ignored when there are two groups and both
paired=TRUEandpaired.lines=TRUE(see the explanation forpoint.paramsandline.paramsbelow).- point.params
For the case when there are two groups and both
paired=TRUEandpaired.lines=TRUE, this is a list containing arguments to the functiongeom_pointthat will be used to plot the points. The default value is an empty list:point.params=list(), in which case the default values forgeom_pointare used, except for the following modification:pch=1.- line.params
For the case when there are two groups and both
paired=TRUEandpaired.lines=TRUE, this is a list containing arguments to the functiongeom_linethat will be used to draw lines between the paired observations. The default value is an empty list:line.params=list(), in which case the default values forgeom_lineare used, except for the following modification:color="gray".- location.params
A list containing arguments to the function
stat_summarythat will be used to plot the estimates of location, i.e.,stat_summaryis called withfun=locationandgeom="point"wherelocationis thelocationargument togeom_stripchartdescribed above. The default value is an empty list:location.params=list(), in which case the default values forstat_summaryare used, except for the following modifications:size=2, position=position_nudge(x = x.nudge)), wherex.nudgeis thex.nudgeargument togeom_stripchartdescribed above.- errorbar.params
A list containing arguments to the function
stat_summarythat will be used to plot the confidence interval, i.e.,stat_summaryis called withfun.data=fun.dataandgeom="errorbar", wherefun.datahas the value"mean_cl_normal"or"mean_cl_boot"depending of the value of the argumentcidescribed above, or, in the case whenlocation="median"fun.datahas the value"median_hilow". The default value is an empty list:errorbar.params=list(), in which case the default values forstat_summaryare used, except for the following modifications:fun.args = list(conf.int = ifelse(location == "mean", 0.95, 0.5)),size = 0.75, width = 0.075, position = position_nudge(x = x.nudge)), wherex.nudgeis thex.nudgeargument togeom_stripchartdescribed above.- n.text
A logical scalar indicating whether to display the sample size for each group. The default is
n.text=TRUE.- n.text.box
A logical scalar indicating whether to surround the text indicating the sample size for each group with a text box (i.e., whether to use
geom_labelinstead ofgeom_text). The default isn.text.box=text.box(see above for the argumenttext.box).- n.text.params
A list containing arguments to the function
stat_n_textthat will be used to display text indicating the sample size for each group. The default value is an empty list:n.text.params=list(), in which case the default values forstat_n_textare used.- location.scale.text
A logical scalar indicating whether to display text indicating the location and scale for each group. The default is
location.scale.text=TRUE.- location.scale.text.box
A logical scalar indicating whether to surround the text indicating the location and scale for each group with a text box (i.e., whether to use
geom_labelinstead ofgeom_text). The default islocation.scale.text.box=text.box(see above for the argumenttext.box).- location.scale.text.params
A list containing arguments to the function
stat_mean_sd_text(whenlocation="mean") or arguments to the functionstat_median_iqr_text(whenlocation="median") that will be used to display text indicating the location and scale for each group. The default value is an empty list:location.scale.text.params=list(), in which case the default values forstat_mean_sd_textorstat_mean_sd_textare used.- test.text
A logical scalar indicating whether to display the results of the hypthesis test comparing groups. The default is
test.text=FALSE.- test.text.box
A logical scalar indicating whether to surround the text indicating the results of the hypothesis test comparing groups with a text box (i.e., whether to use
geom_labelinstead ofgeom_text). The default istest.text.box=text.box(see above for the argumenttext.box).- test
A character string indicating whether to use a standard parametric test (
test="parametric", the default whenlocation="mean") or nonparametric test (test="nonparametric", the default whenlocation="median") to compare groups.- test.text.params
A list containing arguments to the function
stat_test_textthat will be used to display text indicating the results of the hypothesis test to compare groups. The default value is an empty list:test.text.params=list(), in which case the default values forstat_test_textare used, with the exception that the value of the argumenttestin the call tostat_test_textis determined by the value of the argumenttestsupplied togeom_stripchart(see above).
Details
See the vignette Extending ggplot2 at https://cran.r-project.org/package=ggplot2/vignettes/extending-ggplot2.html and Chapter 12 of Wickham (2016) for information on how to create a new geom.
References
Wickham, H. (2016). ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (Use R!). Second Edition. Springer.
See also
Examples
# First, load and attach the ggplot2 package.
#--------------------------------------------
library(ggplot2)
#==========
#---------------------
# 3 Independent Groups
#---------------------
# Example 1:
# Using the built-in data frame mtcars,
# create a stipchart of miles per gallon vs. number of cylinders
# using different colors for each level of the number of cylinders.
#------------------------------------------------------------------
p <- ggplot(mtcars, aes(x = factor(cyl), y = mpg, color = factor(cyl)))
p + geom_stripchart() +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
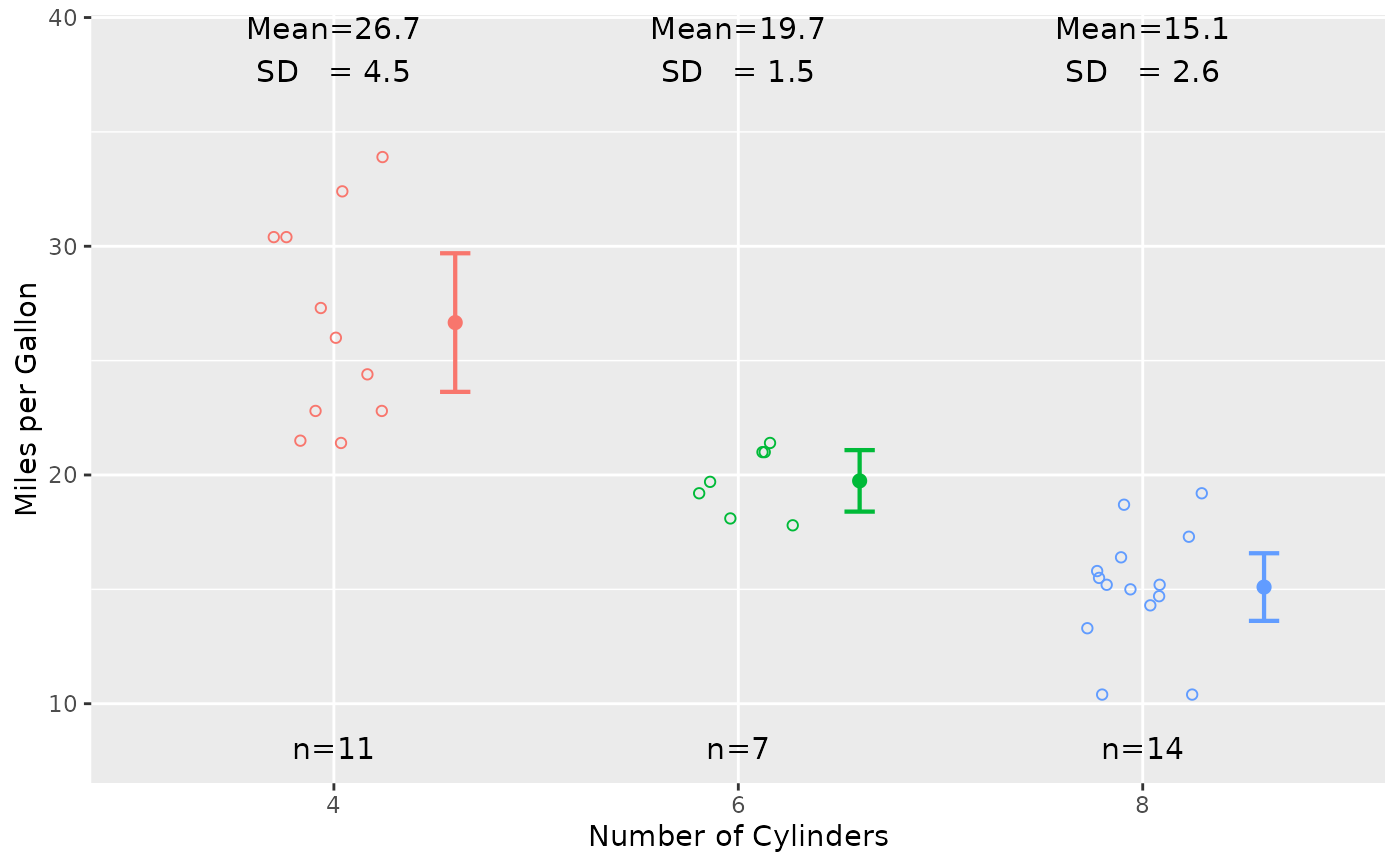 #==========
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
# Example 2:
# Repeat Example 1, but include the results of the
# standard parametric analysis of variance.
#-------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Example 3:
# Using Example 2, show explicitly the layering
# process that geom_stripchart is using.
#
# This plot should look identical to the previous one.
#-----------------------------------------------------
set.seed(47)
dev.new()
p + theme(legend.position = "none") +
geom_jitter(pch = 1, width = 0.15, height = 0) +
stat_summary(fun = "mean", geom = "point",
size = 2, position = position_nudge(x = 0.3)) +
stat_summary(fun.data = "mean_cl_normal", geom = "errorbar",
size = 0.75, width = 0.075, position = position_nudge(x = 0.3)) +
stat_n_text() +
stat_mean_sd_text() +
stat_test_text() +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Example 4:
# Repeat Example 2, but put all text in a text box.
#--------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(text.box = TRUE, test.text = TRUE) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Example 5:
# Repeat Example 2, but put just the test results
# in a text box.
#------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE, test.text.box = TRUE) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Example 6:
# Repeat Example 2, but:
# 1) plot the median and IQR instead of the mean and the 95
# 2) show text for the median and IQR, and
# 3) use the nonparametric test to compare groups.
#
# Note that following what the ggplot2 stat_summary function
# does when you specify a "confidence interval" for the
# median (i.e., when you call stat_summary with the arguments
# geom="errorbar" and fun.data="median_hilow"), the displayed
# error bars show intervals based on estimated quuantiles.
# By default, stat_summary with the arguments
# geom="errorbar" and fun.data="median_hilow" displays
# error bars using the 2.5'th and 97.5'th percentiles.
# The function geom_stripchart, however, by default
# displays error bars using the 25'th and 75'th percentiles
# (see the explanation for the argument ci above).
#------------------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(location = "median", test.text = TRUE) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Clean up
#---------
graphics.off()
rm(p)
#========================================
#---------------------
# 2 Independent Groups
#---------------------
# Example 7:
# Repeat Example 2, but use only the groups with
# 4 and 8 cylinders.
#-----------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p <- ggplot(subset(mtcars, cyl %in% c(4, 8)),
aes(x = factor(cyl), y = mpg, color = cyl))
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Example 8:
# Repeat Example 7, but
# 1) facet by transmission type
# 2) make the text smaller
# 3) put the text for the test results in a text box
# and make them blue.
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE, test.text.box = TRUE,
n.text.params = list(size = 3),
location.scale.text.params = list(size = 3),
test.text.params = list(size = 3, color = "blue")) +
facet_wrap(~ am, labeller = label_both) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Clean up
#---------
graphics.off()
rm(p)
#========================================
#---------------------
# 2 Independent Groups
#---------------------
# Example 9:
# The guidance document USEPA (1994b, pp. 6.22--6.25)
# contains measures of 1,2,3,4-Tetrachlorobenzene (TcCB)
# concentrations (in parts per billion) from soil samples
# at a Reference area and a Cleanup area. These data are strored
# in the data frame EPA.94b.tccb.df.
#
# First create one-dimensional scatterplots to compare the
# TcCB concentrations between the areas and use a nonparametric
# test to test for a difference between areas.
dev.new()
p <- ggplot(EPA.94b.tccb.df, aes(x = Area, y = TcCB, color = Area))
p + geom_stripchart(location = "median", test.text = TRUE) +
labs(y = "TcCB (ppb)")
#==========
# Example 10:
# Now log-transform the TcCB data and use a parametric test
# to compare the areas.
dev.new()
p <- ggplot(EPA.94b.tccb.df, aes(x = Area, y = log10(TcCB), color = Area))
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE) +
labs(y = "log10[ TcCB (ppb) ]")
#==========
# Example 11:
# Repeat Example 10, but allow the variances to differ
# between Areas.
#-----------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE,
test.text.params = list(test.arg.list = list(var.equal=FALSE))) +
labs(y = "log10[ TcCB (ppb) ]")
#==========
# Clean up
#---------
graphics.off()
rm(p)
#========================================
#--------------------
# Paired Observations
#--------------------
# Example 12:
# The data frame ACE.13.TCE.df contians paired observations of
# trichloroethylene (TCE; mg/L) at 10 groundwater monitoring wells
# before and after remediation.
#
# Create one-dimensional scatterplots to compare TCE concentrations
# before and after remediation and use a paired t-test to
# test for a difference between periods.
ACE.13.TCE.df
# TCE.mg.per.L Well Period
#1 20.900 1 Before
#2 9.170 2 Before
#3 5.960 3 Before
#... ...... .. ......
#18 0.520 8 After
#19 3.060 9 After
#20 1.900 10 After
dev.new()
p <- ggplot(ACE.13.TCE.df, aes(x = Period, y = TCE.mg.per.L, color = Period))
p + geom_stripchart(paired = TRUE, group = "Well", test.text = TRUE) +
labs(y = "TCE (mg/L)")
#==========
# Example 13:
# Repeat Example 11, but use a one-sided alternative since
# remediation should decrease TCE concentration.
#---------------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(paired = TRUE, group = "Well", test.text = TRUE,
test.text.params = list(test.arg.list = list(alternative="less"))) +
labs(y = "TCE (mg/L)")
#==========
# Clean up
#---------
graphics.off()
rm(p)
#========================================
#----------------------------------------
# Paired Observations, Nonparametric Test
#----------------------------------------
# Example 14:
# The data frame Helsel.Hirsch.02.Mayfly.df contains paired counts
# of mayfly nymphs above and below industrial outfalls in 12 streams.
#
# Create one-dimensional scatterplots to compare the
# counts between locations and use a nonparametric test
# to compare counts above and below the outfalls.
Helsel.Hirsch.02.Mayfly.df
# Mayfly.Count Stream Location
#1 12 1 Above
#2 15 2 Above
#3 11 3 Above
#... ... .. .....
#22 60 10 Below
#23 53 11 Below
#24 124 12 Below
dev.new()
p <- ggplot(Helsel.Hirsch.02.Mayfly.df,
aes(x = Location, y = Mayfly.Count, color = Location))
p + geom_stripchart(location = "median", paired = TRUE,
group = "Stream", test.text = TRUE) +
labs(y = "Number of Mayfly Nymphs")
#==========
# Clean up
#---------
graphics.off()
rm(p)
} # }
#==========
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
# Example 2:
# Repeat Example 1, but include the results of the
# standard parametric analysis of variance.
#-------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Example 3:
# Using Example 2, show explicitly the layering
# process that geom_stripchart is using.
#
# This plot should look identical to the previous one.
#-----------------------------------------------------
set.seed(47)
dev.new()
p + theme(legend.position = "none") +
geom_jitter(pch = 1, width = 0.15, height = 0) +
stat_summary(fun = "mean", geom = "point",
size = 2, position = position_nudge(x = 0.3)) +
stat_summary(fun.data = "mean_cl_normal", geom = "errorbar",
size = 0.75, width = 0.075, position = position_nudge(x = 0.3)) +
stat_n_text() +
stat_mean_sd_text() +
stat_test_text() +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Example 4:
# Repeat Example 2, but put all text in a text box.
#--------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(text.box = TRUE, test.text = TRUE) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Example 5:
# Repeat Example 2, but put just the test results
# in a text box.
#------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE, test.text.box = TRUE) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Example 6:
# Repeat Example 2, but:
# 1) plot the median and IQR instead of the mean and the 95
# 2) show text for the median and IQR, and
# 3) use the nonparametric test to compare groups.
#
# Note that following what the ggplot2 stat_summary function
# does when you specify a "confidence interval" for the
# median (i.e., when you call stat_summary with the arguments
# geom="errorbar" and fun.data="median_hilow"), the displayed
# error bars show intervals based on estimated quuantiles.
# By default, stat_summary with the arguments
# geom="errorbar" and fun.data="median_hilow" displays
# error bars using the 2.5'th and 97.5'th percentiles.
# The function geom_stripchart, however, by default
# displays error bars using the 25'th and 75'th percentiles
# (see the explanation for the argument ci above).
#------------------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(location = "median", test.text = TRUE) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Clean up
#---------
graphics.off()
rm(p)
#========================================
#---------------------
# 2 Independent Groups
#---------------------
# Example 7:
# Repeat Example 2, but use only the groups with
# 4 and 8 cylinders.
#-----------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p <- ggplot(subset(mtcars, cyl %in% c(4, 8)),
aes(x = factor(cyl), y = mpg, color = cyl))
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Example 8:
# Repeat Example 7, but
# 1) facet by transmission type
# 2) make the text smaller
# 3) put the text for the test results in a text box
# and make them blue.
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE, test.text.box = TRUE,
n.text.params = list(size = 3),
location.scale.text.params = list(size = 3),
test.text.params = list(size = 3, color = "blue")) +
facet_wrap(~ am, labeller = label_both) +
labs(x = "Number of Cylinders", y = "Miles per Gallon")
#==========
# Clean up
#---------
graphics.off()
rm(p)
#========================================
#---------------------
# 2 Independent Groups
#---------------------
# Example 9:
# The guidance document USEPA (1994b, pp. 6.22--6.25)
# contains measures of 1,2,3,4-Tetrachlorobenzene (TcCB)
# concentrations (in parts per billion) from soil samples
# at a Reference area and a Cleanup area. These data are strored
# in the data frame EPA.94b.tccb.df.
#
# First create one-dimensional scatterplots to compare the
# TcCB concentrations between the areas and use a nonparametric
# test to test for a difference between areas.
dev.new()
p <- ggplot(EPA.94b.tccb.df, aes(x = Area, y = TcCB, color = Area))
p + geom_stripchart(location = "median", test.text = TRUE) +
labs(y = "TcCB (ppb)")
#==========
# Example 10:
# Now log-transform the TcCB data and use a parametric test
# to compare the areas.
dev.new()
p <- ggplot(EPA.94b.tccb.df, aes(x = Area, y = log10(TcCB), color = Area))
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE) +
labs(y = "log10[ TcCB (ppb) ]")
#==========
# Example 11:
# Repeat Example 10, but allow the variances to differ
# between Areas.
#-----------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(test.text = TRUE,
test.text.params = list(test.arg.list = list(var.equal=FALSE))) +
labs(y = "log10[ TcCB (ppb) ]")
#==========
# Clean up
#---------
graphics.off()
rm(p)
#========================================
#--------------------
# Paired Observations
#--------------------
# Example 12:
# The data frame ACE.13.TCE.df contians paired observations of
# trichloroethylene (TCE; mg/L) at 10 groundwater monitoring wells
# before and after remediation.
#
# Create one-dimensional scatterplots to compare TCE concentrations
# before and after remediation and use a paired t-test to
# test for a difference between periods.
ACE.13.TCE.df
# TCE.mg.per.L Well Period
#1 20.900 1 Before
#2 9.170 2 Before
#3 5.960 3 Before
#... ...... .. ......
#18 0.520 8 After
#19 3.060 9 After
#20 1.900 10 After
dev.new()
p <- ggplot(ACE.13.TCE.df, aes(x = Period, y = TCE.mg.per.L, color = Period))
p + geom_stripchart(paired = TRUE, group = "Well", test.text = TRUE) +
labs(y = "TCE (mg/L)")
#==========
# Example 13:
# Repeat Example 11, but use a one-sided alternative since
# remediation should decrease TCE concentration.
#---------------------------------------------------------
dev.new()
p + geom_stripchart(paired = TRUE, group = "Well", test.text = TRUE,
test.text.params = list(test.arg.list = list(alternative="less"))) +
labs(y = "TCE (mg/L)")
#==========
# Clean up
#---------
graphics.off()
rm(p)
#========================================
#----------------------------------------
# Paired Observations, Nonparametric Test
#----------------------------------------
# Example 14:
# The data frame Helsel.Hirsch.02.Mayfly.df contains paired counts
# of mayfly nymphs above and below industrial outfalls in 12 streams.
#
# Create one-dimensional scatterplots to compare the
# counts between locations and use a nonparametric test
# to compare counts above and below the outfalls.
Helsel.Hirsch.02.Mayfly.df
# Mayfly.Count Stream Location
#1 12 1 Above
#2 15 2 Above
#3 11 3 Above
#... ... .. .....
#22 60 10 Below
#23 53 11 Below
#24 124 12 Below
dev.new()
p <- ggplot(Helsel.Hirsch.02.Mayfly.df,
aes(x = Location, y = Mayfly.Count, color = Location))
p + geom_stripchart(location = "median", paired = TRUE,
group = "Stream", test.text = TRUE) +
labs(y = "Number of Mayfly Nymphs")
#==========
# Clean up
#---------
graphics.off()
rm(p)
} # }